As rehabilitation medicine and elderly health management become increasingly sophisticated, "fall risk assessment" is becoming a keyword that attracts much attention. Especially among the elderly, falling is no longer a small problem - it is often a "turning point" that causes fractures, hospitalization, deterioration of mobility, and even long-term bed rest and a sharp decline in quality of life.
So, is there a more scientific and quantifiable way to issue a warning signal before a fall occurs?
The answer is: Yes. Gait analysis and assessment instruments are currently one of the most scientific and clinically valuable tools for assessing fall risk.
1. Fall risk is not a "luck problem", but a comprehensive expression of "dynamic ability"
Falling is not accidental, and it often hides some hidden dangers of the human movement system, such as:
Unstable gait, poor center of gravity control
Decreased lower limb muscle strength
Slow reaction or poor coordination
Decreased cognitive and balance ability
And these indicators are difficult to accurately assess based solely on subjective descriptions or doctor's naked eye observations. Therefore, an efficient, objective, and repeatable assessment method is needed to "quantify the risk", which is exactly the advantage of gait analysis and assessment instruments.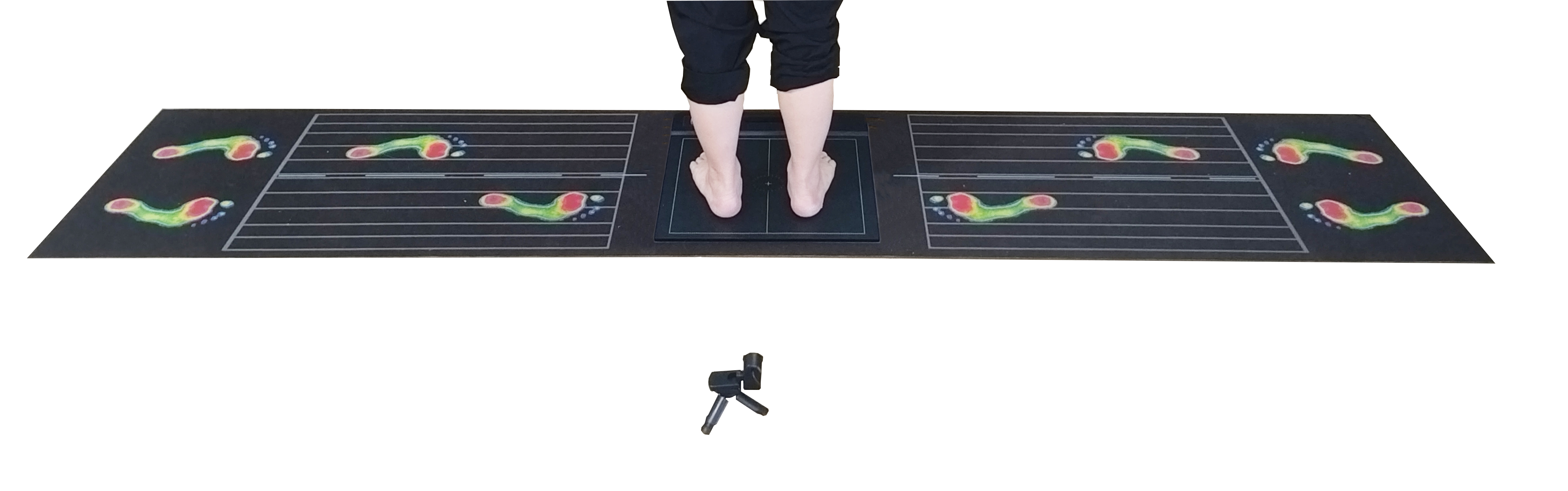
2. What is a gait analysis and assessment instrument?
Gait analysis and assessment instruments are a type of intelligent device that combines high-precision sensors, computer vision algorithms and sports biomechanical models. It dynamically measures the user's walking posture, standing state, plantar reaction, step frequency and stride and other key parameters to establish a complete sports function assessment system.
Common forms include:
Pressure sensing gait board: collects the order of foot landing, pressure distribution, center of gravity transfer trajectory, etc.
Intelligent insole system: can record pressure changes and footsteps rhythm during daily walking
3D motion capture system: analyzes the coordination of various joints and gait characteristics of the body through cameras
Center of gravity swing test: evaluates static balance and standing stability
3. Deep correlation between gait analysis and fall risk assessment
The assessment of fall risk must be based on a series of "dynamic biomechanical parameters". The following key data collected by the gait analysis and assessment instrument are scientific indicators of fall risk:
1. Changes in step length and cadence
Old people or people with neurological disorders often show a phenomenon of "broken steps" with shorter step length and faster cadence, which is a typical manifestation of insufficient trunk stability and fear of falling.
2. The ratio of the time when both feet are on the ground
Healthy individuals usually support themselves on one foot for a longer time, while people at high risk of falling will increase the time when both feet are on the ground at the same time to seek "multi-point support".
3. Center of gravity transfer trajectory
By observing the center of gravity deviation path through the induction board or insole system, it can be determined whether the balance ability during standing and walking has decreased.
4. Gait symmetry analysis
Whether the left and right gait rhythms are consistent, whether the force is balanced, and whether the hip and knee joint range of motion is consistent, all of these can indicate whether there is "compensatory deviation" and increase the risk of falling.
5. Standing stability index
By measuring the body swing amplitude and frequency during static standing, the "standing control ability" can be evaluated. The larger the swing, the worse the balance.
These quantitative indicators can not only be used for clinical judgment, but also generate intuitive chart reports, which are convenient for doctors to formulate intervention plans and patients to understand their own status.
4. Real Case: How to Prevent Accidents Before They Happen?
Take a nursing home as an example. There were many falls among the elderly in one year. Since the introduction of gait analysis and assessment instruments, the institution has conducted a dynamic gait assessment on elderly residents every quarter:
The system found that some elderly people had abnormal data of "short right foot support time and outward center of gravity"
Combined with balance training, lower limb strength improvement courses and personalized assistive device intervention
The incidence of falls decreased by more than 70% within one year
This shows that scientific detection + early intervention is an effective way to avoid falls
5. Gait analysis is not "the end of the test", but the "starting point of prevention"
A mature gait analysis system should not only stay at the "assessment" level, but also become one of the closed loops of health management:
Early screening: identify risk groups, focusing on the elderly, postoperative, and rehabilitation individuals
Intervention in the middle: formulate personalized plans such as muscle training, balance exercises, and insole customization
Late tracking: observe the intervention effect and adjust the plan through periodic testing
Especially for community nursing homes, rehabilitation hospitals, and posture management centers, the gait analysis system is no longer an "optional" but a "standard configuration".
Falling is not accidental, but a signal from the body. To understand this signal, scientific tools are needed.
Gait analysis and assessment instruments are our key assistants in understanding the body's dynamic ability and scientifically judging the risk of falling. It not only "sees the problem", but also "quantifies the risk", providing a basis for decision-making support for rehabilitation, prevention, and training.
Today, when health management is becoming more and more "front-end", fall prevention should also shift from "post-processing" to "pre-warning". And this is the real value of the gait analyzer.

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-06-30
2025-06-30 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192