As foot health management becomes increasingly sophisticated, the word "scanning" has gradually entered the lives of ordinary people. Whether it is for modeling corrective insoles, or for shoe customization, rehabilitation assessment, and foot database construction, "foot scanning" is being adopted by more and more institutions and brands. Among the many devices, the comparison between the 3D foot scanner and the 2D scanner has become the focus of many people's attention.
They all seem to be tools for "scanning feet", but from the technical principle to the depth of application, the difference between the two is far greater than you think.
1. Technical principle: 2D is plane capture, 3D is stereo reconstruction
As the name suggests, 2D foot scanners can only obtain a flat image of the sole of the foot. This type of equipment is mostly based on high-definition cameras or optical tablets. By shooting the sole contour, it captures information such as foot length, foot width, and footprint shape. It is suitable for some basic measurement scenarios, such as ordinary shoe size recommendations, simple insole cutting suggestions, etc.
The 3D foot scanner uses a more advanced laser scanning modeling technology. The device emits a high-density laser grid to illuminate the surface of the foot, and uses a multi-angle high-definition sensor to capture reflected light. The system then quickly calculates the spatial coordinates of each part of the foot based on the time difference and angle change of light reflection, and completely restores a three-dimensional model.
This principle is derived from the mature technology of industrial-grade surveying and medical modeling. It is non-contact, interference-free, and high-precision, and is truly "fine foot collection".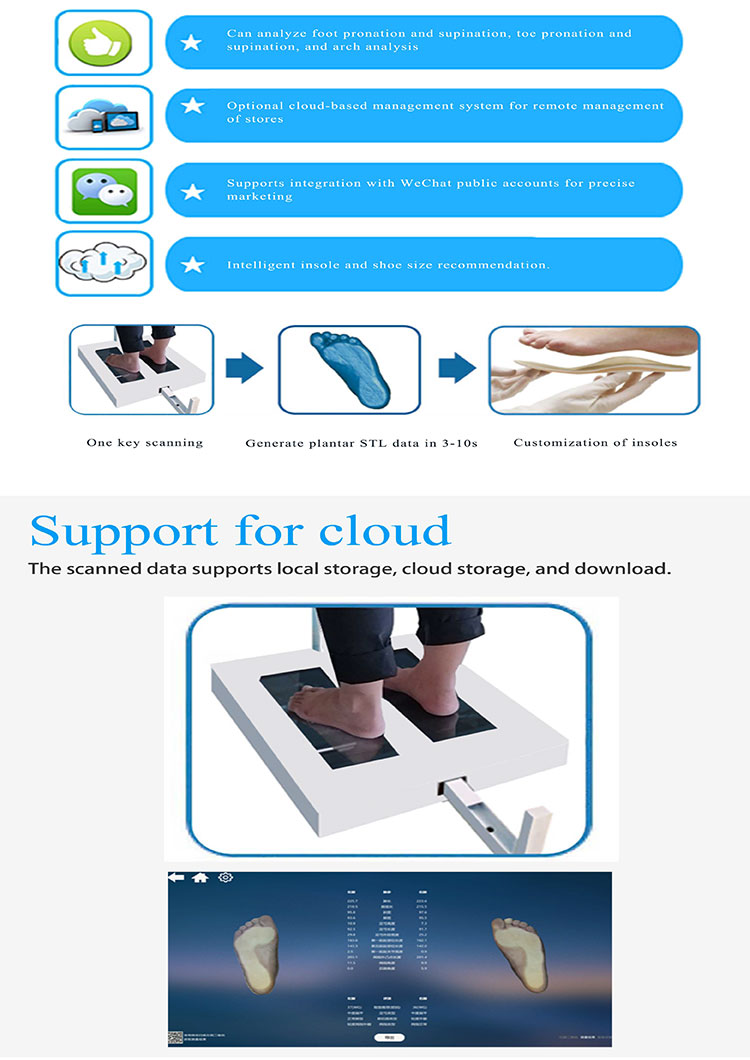
2. Data dimension: 2D data is limited, and 3D models are more complete
The data dimension of a 2D scanner is extremely limited. It mainly outputs a projection image of the sole of the foot - you can see the shape, width, and length of the footprint, and at most can only estimate the outline of the arch area. However, this type of image is the result of "flattening" and cannot reflect important structures such as the height of the instep, the true ups and downs of the arch, the arrangement of the toes, and the inclination of the heel.
The output of a 3D scanner is a complete spatial data model. Not only can you look at it from above, from the side, and from an oblique angle, you can also directly export the foot in 3D formats such as STL, OBJ, and WRL for:
Medical orthopedic analysis (such as high arch and flat foot assessment)
Insole and shoe last design modeling
Personalized 3D printing solution
Dynamic posture comparison and foot symmetry analysis
In short, 2D is measurement and 3D is reconstruction. The amount of information in the latter is much higher than that of the former.
3. Usage scenario: simple recommendation vs. personalized customization
If you just want to determine what shoe size to wear and whether you need insoles, most 2D devices are enough. But if your goal is to customize insoles, conduct foot intervention, rehabilitation tracking, and disease assessment, then 2D is obviously not enough.
For example, in the field of foot orthopedics, doctors often need:
Arch height and span data
Instep structure and phalangeal arrangement
Heel inversion and inversion tilt angle
Whether the foot shape is symmetrical
These cannot be obtained from 2D images and can only be extracted finely by three-dimensional models.
Similarly, in customized shoes, insole matching, and sports support products, the accuracy of three-dimensional scanning directly determines the fit and comfort of the product.
IV. Equipment performance: scanning time, accuracy, and docking capabilities are comprehensively improved
Modern 3D foot scanners (such as the Jingyi Xun series) not only have a measurement accuracy of ±0.5mm, but also only take more than ten seconds to scan a pair of feet. They also support multi-format export and cloud synchronization, and can seamlessly connect insole design software, CAD systems, 3D printing equipment, etc.
However, 2D scanners are limited to image output, lack further modeling capabilities, and have obvious data island effects, making it difficult to support intelligent and digital shoemaking and rehabilitation workflows.
V. Actual value: Three-dimensional is not only accurate, but also a basis for decision-making
From the perspective of consumer experience, 2D scanning can usually only "suggest", while 3D scanning can "guide". For example:
When customizing insoles, 2D scanning can only tell you that the arch is low, but 3D scanning can accurately locate the arch sinking degree, width, and support points, and directly use it for module cutting and printing path formulation
During the shoe fitting process, the 3D model can compare the fit between different brands of shoe lasts and foot shapes, greatly improving the accuracy of recommendations and reducing returns and exchanges
This is why more and more customized service providers, e-commerce platforms, and medical rehabilitation institutions choose to invest in 3D scanners instead of continuing to rely on 2D images.
If 2D scanning "opens the door" for foot measurement, then 3D scanning truly paves a digital highway for foot health management.
It is not only more accurate, but more importantly, it can "see the essence, reconstruct solutions, and upgrade services." In all future scenarios that emphasize "personalization, customization, and digitalization," 3D plantar scanners will become irreplaceable central equipment.
So, it's not that 2D is bad, but when you need higher-level and more accurate foot services, 3D is the right starting point.

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-06-30
2025-06-30 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192