When comparing the differences between a “pressure platform” and a “3D foot scanner” in terms of accuracy for evaluating flat feet, we should break the question down into two main parts: the target of measurement and the purpose of diagnosis.
The measurement principles, output variables, and clinical indications of the two types of devices are fundamentally different; therefore, which one is “more accurate” depends on whether we want morphological information or functional-mechanical information.
First, distinguishing from the perspective of technology and output:
A foot 3D scanner uses non-contact optical methods such as laser or structured light, mainly to reconstruct the three-dimensional geometric morphology of the foot (for example, foot length, foot width, arch height, and volume). Under static standing conditions, the spatial resolution for quantifying arch morphology is high, with good repeatability, and it is suitable for orthotic and insole design as well as morphological follow-up. 3D surface scanning is used for geometric reconstruction of foot shape, and it has good reliability and clinical applicability.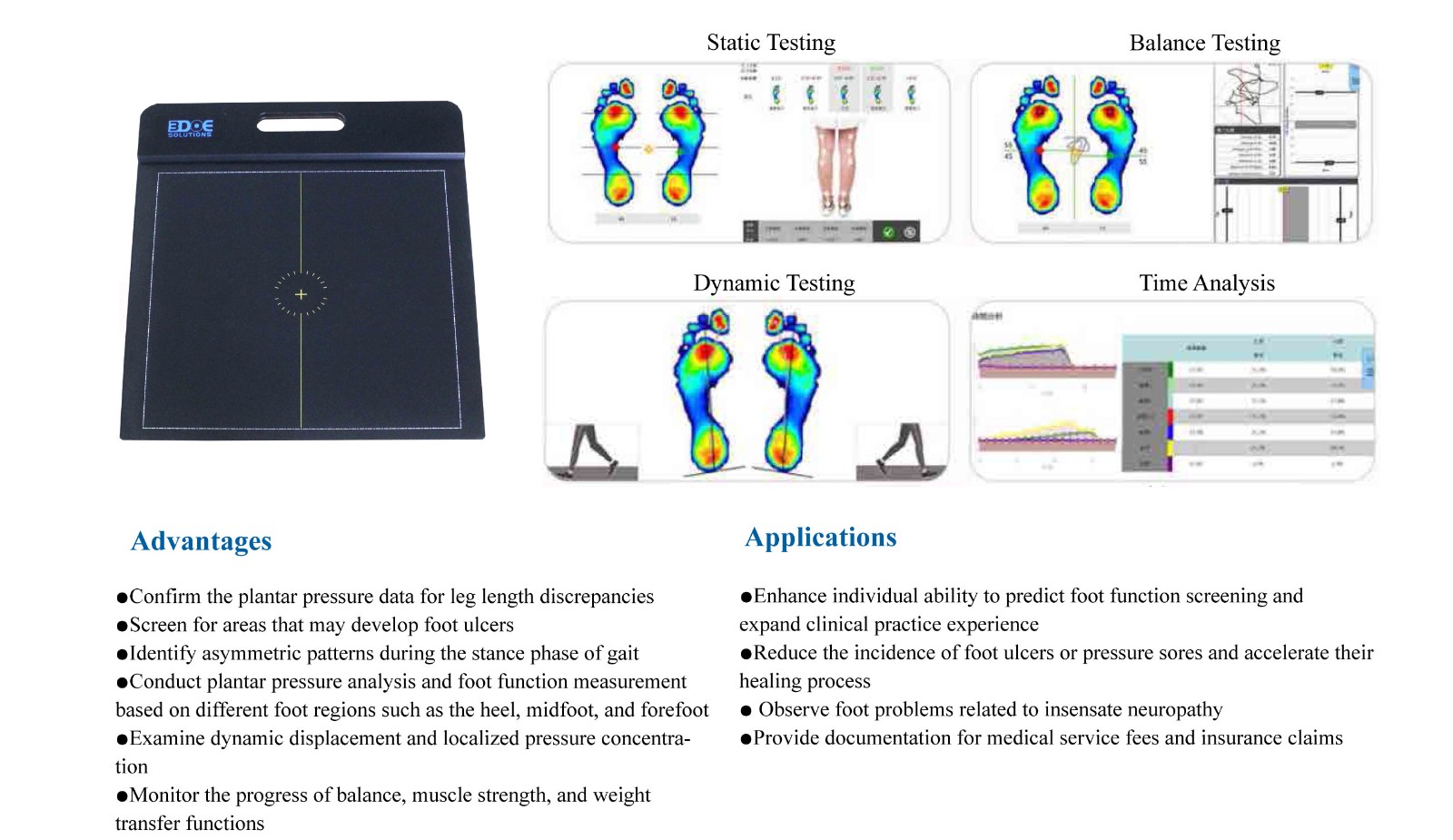
Second, a plantar pressure platform is based on a contact sensor array and directly records the mechanical distribution during foot–ground contact (peak pressure, contact area, center of pressure trajectory, and the changing pattern of the force-time curve), and it can reflect dynamic loading characteristics during the gait cycle.
Therefore, the pressure platform has greater diagnostic value in identifying increased midfoot loading, assessing functional arch collapse during walking or running, and determining high-risk pressure points (such as in diabetic feet), and some of its parameters also have more research evidence supporting test–retest reliability.
Next, in terms of judging accuracy based on the clinical meaning of “flat feet”: flat feet can be divided into structural (anatomical low arch) and functional (arch collapse during weight-bearing or movement) types.
If the purpose is to determine static arch height or to manufacture customized orthotics, 3D scanning is more “direct” and precise because it can quantitatively measure arch geometry.
If the purpose is to evaluate gait function, the arch’s load-bearing capacity under weight-bearing, or to determine dynamic collapse, the pressure platform can more realistically reflect clinically relevant functional changes and risk indicators. Many studies show that static geometry and dynamic loading do not correspond one-to-one, so a single technology has limitations in diagnosis.
In addition, accuracy is also influenced by several variable factors: equipment calibration and resolution, standardization of posture or gait during data collection, whether multiple repeated measurements are performed, back-end algorithms (such as the definition of arch height or the method of pressure segmentation), and the consistency of the examiner’s operation.
Low-cost or commercial simplified devices may differ significantly from medical-grade equipment in terms of precision and threshold settings, which may in turn affect the final diagnostic conclusion.
The optimal clinical strategy is to combine the two: use 3D scanning to obtain an accurate morphological baseline, and then use a pressure platform to verify the loading performance in standing and walking conditions, in order to achieve mutual confirmation between morphology and function, making the diagnosis of flat feet more comprehensive and accurate.

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-10-15
2025-10-15 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192