Gait analysis systems, utilizing plantar pressure measurement, have a scientific basis for evaluating conditions such as flat feet and high arches, but they do not equate to clinical diagnosis. The specific analysis is as follows:
I. Fundamental Principles
Gait analysis systems use pressure sensors or pressure plates to collect data on pressure distribution, contact area, and the trajectory of the center of gravity during standing and walking.
Flat Feet: Arch collapse, increased contact area on the inner foot, pressure shifted inward, and gait characteristics such as foot inversion or insufficient propulsion.
High Arches: Excessively high arches, reduced contact area, pressure concentrated between the heel and forefoot, and gait characteristics such as concentrated impact and poor elasticity.
This system, by quantifying pressure distribution and arch index, can assess whether the arch is low or high, thereby providing a preliminary evaluation of the likelihood of flat feet or high arches.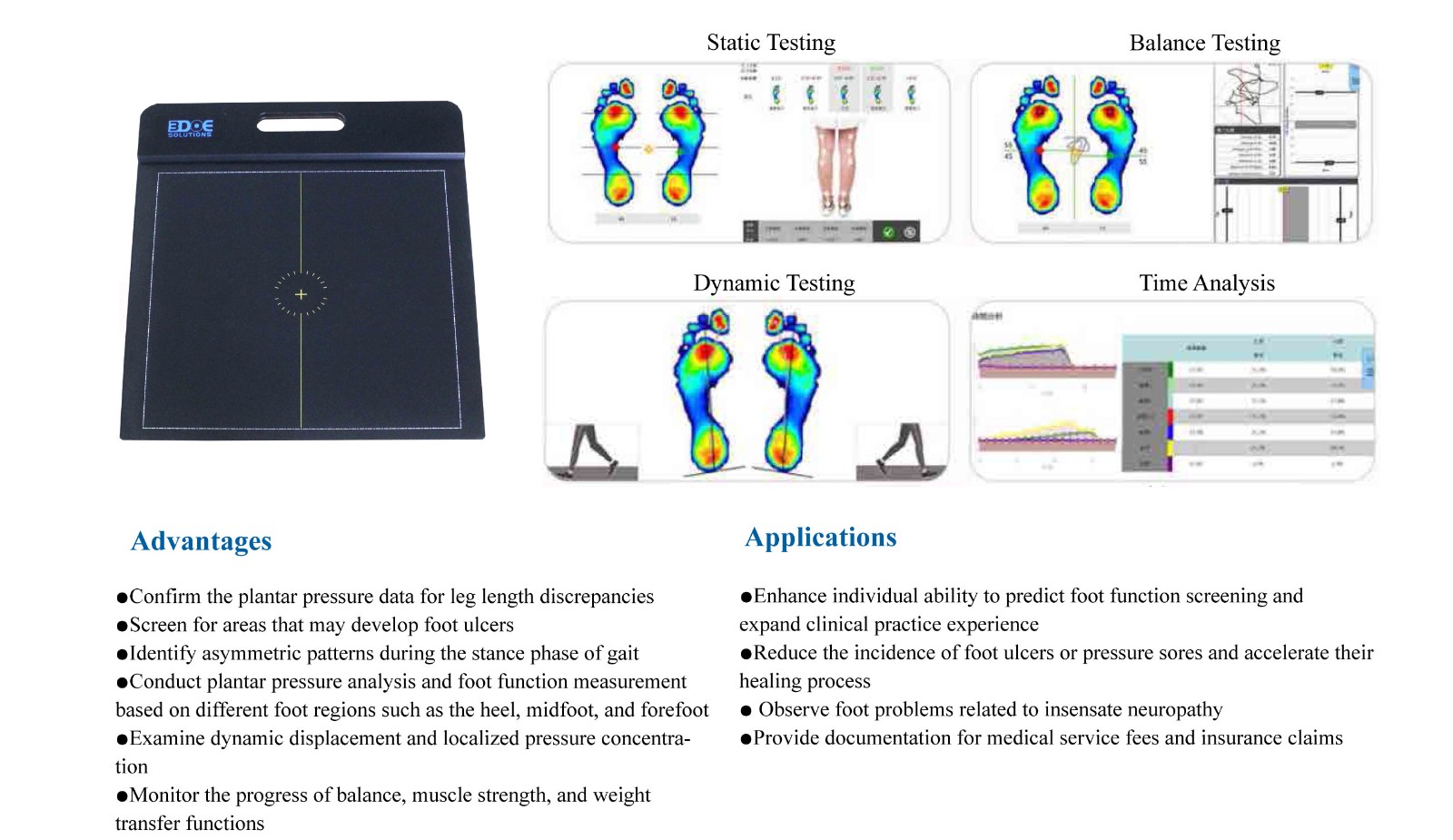
II. Accuracy and Limitations
Advantages:
Can quickly and non-invasively obtain dynamic pressure distribution.
Useful for preliminary screening of both adults and children.
Can analyze symmetry and load distribution by comparing the left and right feet.
Provides reference data for rehabilitation, sports training, or insole customization.
Limitations:
Cannot independently diagnose flat feet or high arches; clinical evaluation is required.
Flexible flat feet or temporary changes in foot shape (e.g., due to fatigue) may affect data.
Cannot provide information on arch height, bone structure, or ligament elasticity.
Pediatric arch development data should be interpreted with caution.
III. Applicable Scenarios
Sports stores or shoe shops: Assist with insole recommendations and shoe selection.
Rehabilitation or orthopedic centers: Conduct gait analysis and evaluate rehabilitation training plans.
Children's foot shape monitoring: Track the development trend of foot arches.
Diabetic feet and plantar pressure management: Assess high-pressure areas and risk points.
By combining gait analysis systems with plantar pressure measurement, it can effectively assess the trends of flat feet and high arches. However, it is a preliminary screening and reference tool, not a substitute for imaging and clinical diagnosis. For professional evaluation or treatment decisions, it should be combined with arch height measurements, X-rays, or foot doctor examinations.

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-10-10
2025-10-10 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192