The Principle and Significance of Gait Analysis Instruments in Measuring Plantar Pressure
I. Principle: Basic Principle of Gait Analysis Instruments for Measuring Plantar Pressure
Gait analysis instruments measure plantar pressure mainly by relying on an array of pressure sensors. These sensors collect real-time vertical pressure distribution data from the soles of the feet during walking or standing, reflecting the force interaction between the human body and the ground.
Common pressure measurement principles include:
Force Sensing Resistor (FSR) Principle
This principle measures pressure by detecting changes in material resistance caused by applied force. It has low cost and fast response, and is widely used in commercial applications.
Capacitive Sensing Principle
Composed of two conductors and an intermediate dielectric layer, this method measures pressure based on the change in capacitance caused by variation in distance between the conductors when pressure is applied. It offers good stability and strong resistance to interference.
Piezoelectric Sensing Principle
This method uses piezoelectric materials that generate electric charge when deformed by force. It provides high sensitivity and precision, and is suitable for high-accuracy gait research.
Shear Force Monitoring (Advanced Systems)
Some high-end gait analysis systems can also monitor horizontal shear forces, such as foot sliding and friction during ground contact, to provide a more comprehensive assessment of gait biomechanics.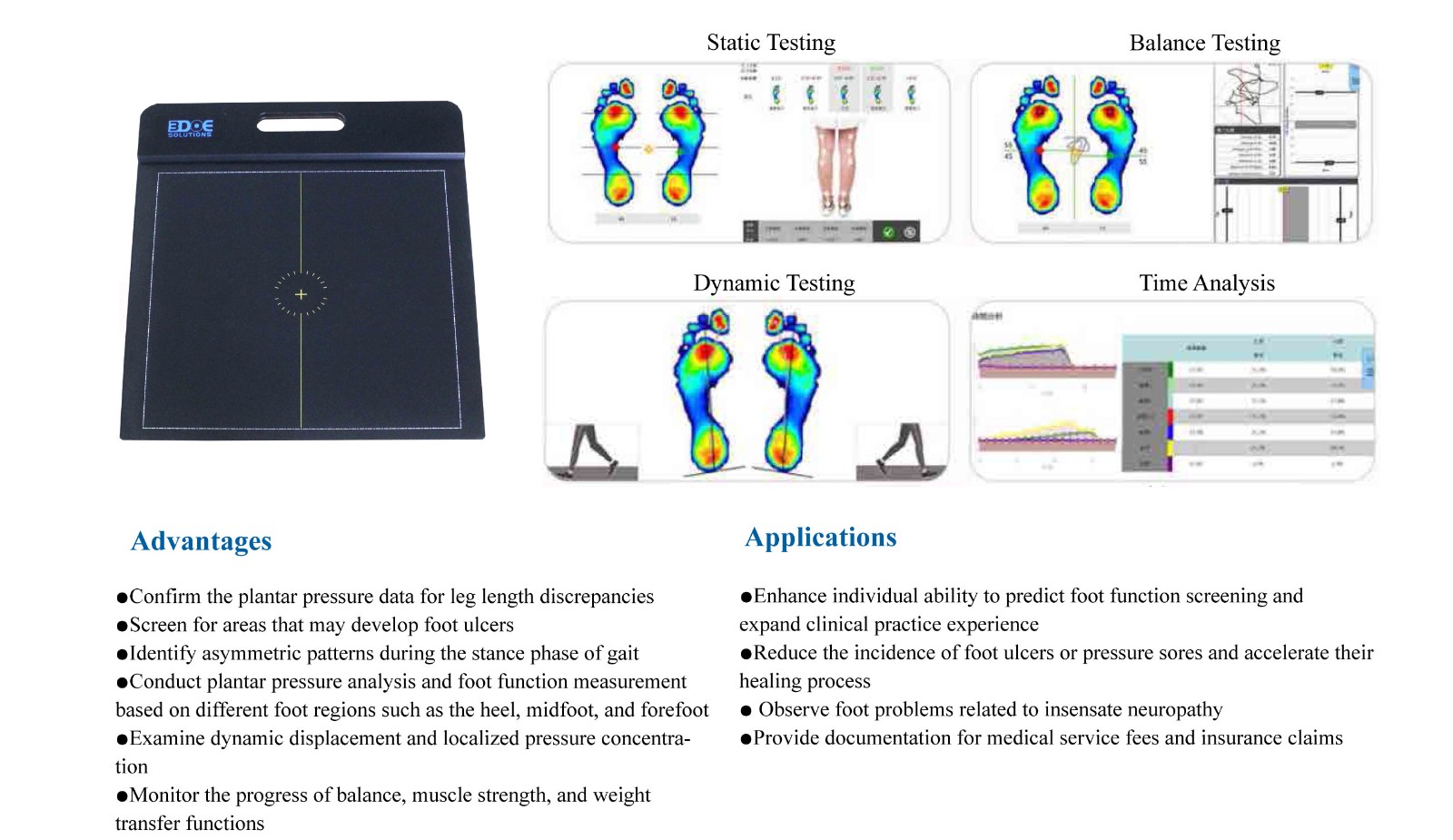
II. Significance: Practical Significance of Measuring Plantar Pressure
Assessing Gait Stability and Symmetry
By comparing pressure areas, contact sequence, and force differences between the left and right feet, it is possible to determine whether an individual's walking is balanced and stable. This helps identify abnormal gaits such as hemiplegic or habitual limping patterns.
Detecting Structural and Functional Foot Abnormalities
Pathological foot types like flat feet, hallux valgus, and rearfoot varus often exhibit characteristic abnormal pressure distributions, which can be visually identified through pressure maps.
Assisting Rehabilitation Evaluation and Orthotic Design
For patients with hemiplegia after stroke, amputations, or spinal cord injuries, plantar pressure data can be used to evaluate rehabilitation outcomes and optimize the fit of assistive devices such as braces or prosthetics.
Optimizing Athletic Performance and Footwear Design
In sports science, plantar pressure data helps analyze the force distribution during running, jumping, and other athletic movements, guiding improvements in technique and the design of customized footwear.
Providing Dynamic and Quantitative Diagnostic Evidence
Compared to traditional observation methods, pressure data offers continuous and objective numerical information, which can be used for long-term monitoring and comparative analysis, thereby improving diagnostic accuracy.

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-07-15
2025-07-15 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192