As foot health gains increasing attention, many rehabilitation centers, sports facilities, and custom insole studios have introduced various types of “cutting-edge” equipment. Among them, two commonly mentioned devices are the 3D foot scanner and the plantar pressure distribution system.
At first glance, they both seem to be “scanning feet,” but in fact, they focus on completely different dimensions, collect different types of data, and are applied in different scenarios. Today, let’s use one article to clearly explain the true differences between these “two stars beneath your feet.”
First, what exactly does a 3D foot scanner scan?
It’s more like taking a three-dimensional photograph of your feet. Using laser or infrared technology, it quickly scans the foot to capture multiple structural parameters, such as instep height, foot length and width, arch shape, hallux (big toe) angle, and toe deformities like hallux valgus.
It’s a static measurement, meaning you don’t need to move — just stand on the scanner or place your foot into the device. Within a few seconds, it generates a complete 3D model of your foot. This model can be used not only to assess whether your foot structure is standard or needs correction, but also to assist in customizing insoles, shoe lasts, foot rehabilitation products, and more.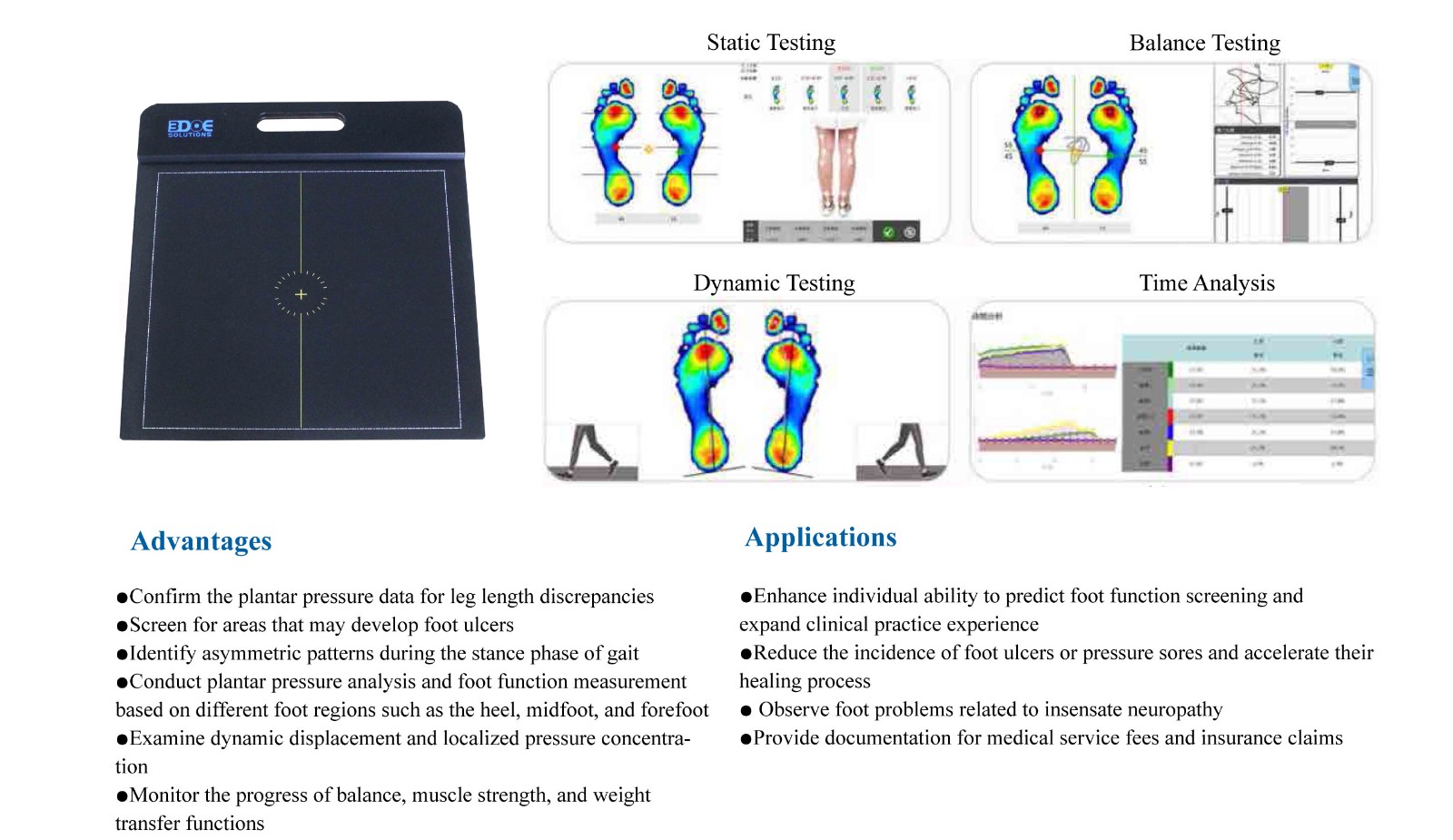
Typical application scenarios include:
Design of insoles, custom shoes, and orthopedic footwear
Evaluation of structural issues like hallux valgus, flat feet, and high arches
Tracking foot development in children
Foot shape data archiving and big data analysis
Now let’s look at the plantar pressure distribution system, which focuses on:
How each area of the sole bears weight when you are standing or walking.
This system usually consists of a sensor mat or pressure plate. The person being examined stands still or walks across it, and the system records real-time changes in plantar pressure, center of gravity shifts, left-right foot load comparisons, gait cycles, and more.
This is dynamic detection, with a focus on simulating your real-life standing and walking patterns to identify potential biomechanical issues.
Typical application scenarios include:
Gait abnormality assessment (such as hemiplegia, post-operative recovery, fall risk in the elderly)
Detection of pelvic tilt and gait asymmetry
Optimization of athletic performance and early warning of chronic injuries
Comparison of rehabilitation progress and assessment of training programs
In one sentence, the difference between the two is:
3D foot scanner — analyzes the "shape" of your foot
Plantar pressure distribution system — analyzes the "load" and "dynamic behavior" of your foot
The two are not in conflict — rather, they complement each other. One captures static structure, the other analyzes dynamic function, together forming a more comprehensive foot health assessment system.
For institutions, if you want to offer clients, patients, or students a systematic foot evaluation solution, these two devices are definitely a “golden pair” worth considering.

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-06-20
2025-06-20 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192